 Lesson 3
Lesson 3
What is sustainable development?
The term "sustainable development" refers to the internationally recognized model for the sustainability of our global community. Important social issues such as culture, social interaction and economic potential should be reconciled in an environmentally-friendly and nature-preserving manner.
What is Education for Sustainable Development?
Education for Sustainable Development (ESD) teaches children, young people and adults sustainable thinking and action. It enables people to make decisions for the future and to assess how their own actions will affect future generations or life in other regions of the world (German Commission for UNESCO registered association, 2013). ESD aims to impart various competencies that enable learners to reflect and make conscious decisions in complex situations (with economic, ecological and social causes). These competencies are summarized as cognitive skills.
These cognitive skills include, for example:
- Thinking and acting with foresight
- Interdisciplinary learning
- Reflection on one's own principles and the principles of others
- Empathy and solidarity with others
- Participation in decision-making processes
de Haan & Harenberg, 1999
A process-oriented and open understanding of education in ESD requires to a large extent the use of participative methods. This fosters learners' skills for conscious social participation.
Introduction: SDGs
With the signing of Agenda 2030 in September 2015, the international community aims to transform our society. It is believed that countries must meet the global challenges together if they are to create a sustainable, ecologically compatible, socially just and economically efficient world.
The key principles guiding action are categorised into 5 core areas: People, planet, prosperity, partnership, peace. These principles are inextricably linked. All dimensions of sustainable development – social-environmental economy – are therefore taken up and taken into account in the Agenda.
In order to implement Agenda 2030, the United Nations has formulated 17 sustainability goals, the so-called SDGs (Sustainable Development Goals). These key objectives should form the basis of all action and are designed as a verifiable catalogue of objectives.
While the UN's 8 Millennium Development Goals in 2000 mainly addressed countries in the Global South, the SDGs apply to all countries. The UN strives for economic growth in all countries and combines this goal with environmental and climate protection goals. The guiding principle is that progress cannot be achieved without taking our planetary boundaries into account.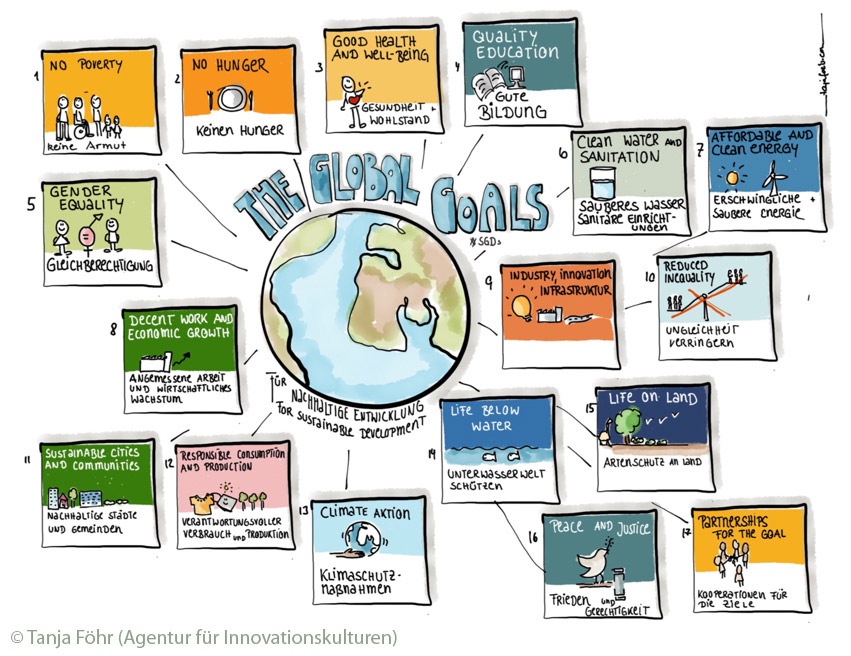
Task
|
Look at the SDGs in the graphic again. Which of the targets are particularly relevant for dealing with large predators? Can you identify any goals that may be contradictory? To help you, you can first assign the goals to the 4 categories "Politics, Economy, Society, Planet". |










